The cavity is the space enclosed by the hollow bone and muscular organs that protect the vital organs. The abdominal cavity is the largest cavity in the human body. It lies in between the thoracic cavity and the Pelvic cavity. The abdominal cavity is oval in shape and consists of organs of the digestive system. The lining of the abdominal cavity by the serous membrane is known as the peritoneum. The outer lining is the parietal peritoneum. The inner lining of organs is the visceral peritoneum. The space between these two peritoneum is the peritoneal cavity.
Abdominal cavity organs
The abdominal cavity consists of organs of the digestive system and renal system.
- Liver
- Stomach
- Biliary tract
- Gall bladder
- Stomach
- spleen
- Pancreases
- Bladder
- Adrenal glands
- Kidneys
- Appendix
- Small intestine
- Duodenum
- Ileum
- Jejunum
13. Large intestine
- Ascending colon
- Transverse colon
- Descending colon
Borders and boundaries of the abdominal cavity
The abdominal cavity lies in between the thoracic cavity and pelvic cavity where the diaphragm separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity, which is a thin sheet of connective tissue assisting in respiration. The pelvic floor of the true pelvic cavity separates the pelvic and abdominal cavity. Here are some mentioned boundaries.
Anteriorly: The abdominal muscle is present anterior to the abdominal cavity. The abdominal muscle consists of the rectus muscle, Internal and external oblique muscle, and transverse muscle.
Posteriorly: The posterior abdominal muscle and the vertebral column are present posterior to the abdominal cavity.
Laterally: The part of the abdominal muscle and lower ribs (false and floating ribs) are present on both lateral sides of the abdominal cavity.
Superiorly: The superior border of the abdomen is the diaphragm which is a domeshape muscle that attaches to the sternum that plays an important role in respiration.
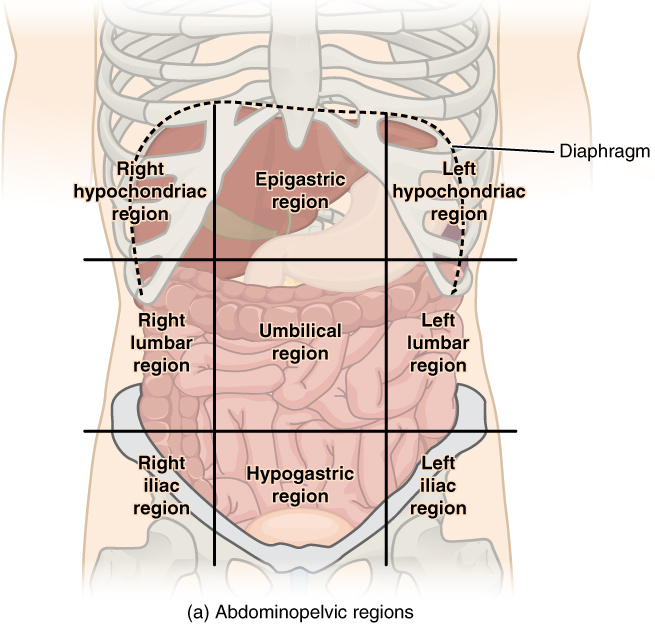
9 regions of the abdomen
The abdomen is divided by the imaginary line for the medical examination. These describe the position of organs and the different structure it contains. The core is divided into 2 vertical and 2 imaginary lines. The vertical line is up to mid-lingual ligaments from the midclavicular line. The horizontal line is drawn from the 10th costal cartilage level and hip bone. With the help of these 4 imaginary lines abdominal cavity is divided into nine regions of the abdomen that are mentioned below.
- Right hypochondriac region
- Epigastrium region
- Left hypochondriac region
- Right lumbar region
- Umbilical region
- Left lumbar region
- Right iliac region
- Hypogastrium region
- Left iliac region
Abdominal cavity Organs
- Right hypochondriac region:
Most of the liver, gall bladder, Biliary tract, some part of the small intestine, hepatic flexion of the colon. - Epigastrium region:
Left lobe of the liver, pancreas, part of duodenum spleen, and adrenal glands. - Left hypochondriac region:
Spleen, splenic flexure of the colon, part of the pancreas. - Right lumbar region:
Right kidney, part of the gall bladder, and ascending colon. - Umbilical region:
Umbilicus, part of the small intestine and pancreas. - Left lumbar region:
Left kidney, left adrenal glands, descending colon. - Right iliac region:
Vermiform appendix, caecum - Hypogastrium region:
Urinary bladder, Uterus - Left iliac region:
Sigmoid colon
Abdominal Pain
Abdominal pain is a common discomfort in the abdominal region offering a wide variety of differential diagnoses with different organs like the kidney, Liver, and Stomach. The pain in the stomach can be caused by various factors like different organ inflammation or any other disorder. The abdominal pain may be either parietal, visceral, or referred pain. The common causes of abdominal pain include Food poisoning, Constipation, Gastritis, Enteritis, Appendicitis, Cholelithiasis, Cholecystitis, Peritonitis, Pancreatitis, Renal calculus, Gastroenteritis, protozoal diseases like Amoebiasis, and others like Hepatitis, Ascites, Intussusception, etc.
With the division of the quadrant and nine regions of the abdomen, the diagnosis of abdominal pain has been a little bit easier as different regions indicate different organs. The differential diagnosis of abdominal pain according to pain in different regions,
Differential diagnosis according to location.
- Right hypochondriac region:
Pain in these regions indicate the differential diagnosis related to organs like the liver, gall bladder, and biliary tract showing differential diagnosis like Acute cholecystitis, Liver abscess Cholelithiasis, and Hepatitis. - Epigastrium region
The differential diagnosis of the epigastrium is gastritis, Peptic ulcer disease, gastric ulcer, pancreatitis, and duodenal ulcer. Epigastrium pain also relates to the heart so pericarditis and myocardial infarction can be the cause. - Left hypochondriac region
The differential diagnoses of the left hypochondriac region are GERD, gastric ulcer, splenic cyst, etc. - Right lumbar region
The differential diagnosis of the Right lumbar region pain are Nephrolithiasis ( renal or kidney stone) and pyelonephritis ( infection of the kidney). - Umbilical region
The differential diagnosis of pain in the umbilical region is pancreatitis, gastritis, gastroenteritis, Peptic ulcer disease, Bowel obstruction, and Celiac disease. - Left lumbar region
The differential diagnoses of the left lumbar pain are splenic cyst, Enteritis, bowel obstruction, Nephrolithiasis, and pyelonephritis. - Right iliac region
The differential diagnosis of the pain in the right iliac fossa is Appendicitis(The most common, pain at the McBurney point ), Bowel obstruction, and Inguinal hernia. - Hypogastrium region
The differential diagnoses of the pain in the hypogastrium region are Diverticulitis, Colitis Cystitis, and Urinary Tract infection. - Left iliac region
The differential diagnosis of the left iliac region pain are Diverticulitis, Colitis, Inflammatory bowel disease etc.
Pain in lower right abdomen
The pain in the lower right quadrant of the abdomen is due to Intussusception, Bowel obstruction, Appendicitis, Nephrolithiasis, Pyelonephritis, Cystitis, Urinary tract infection, and cystic stones, also includes gynecological problems like ectopic pregnancy, ovarian cyst, fibroid, endometrial cancer, etc.
Pain in lower left abdomen
The pain in the lower left abdomen or lower quadrant of the abdomen is due to Toxic megacolon, Sigmoid colon volvulus, Diverticulitis Bowel obstruction Nephrolithiasis, etc.
Pain in upper Right Abdomen
The pain in the upper right abdomen is due to Hepatomegaly, hepatitis, Liver cancer, Liver abscess, gallstone, worm infection, bowel obstruction, etc
Abdominal Examination
There are 4 quadrants of the abdomen.
- Right upper quadrant
- left upper quadrant
- Right lower quadrant
- left lower quadrant
and nine regions of the abdomen, there is the process of examining the patient for abdominal examination. There are 4 steps of abdominal examination as follows.
- Inspection
- Palpation
- Percussion
- Auscultation
Before examining the patient for abdominal examination, Consent from the patient is important. Screening of patients’ bodies for privacy under good and warm surroundings. The patient lies in the supine position. The patient’s body from the Xiphisternum to the upper thigh should be exposed only the procedure of examination can be started.
Inspection
- Inspect the patient’s shape of the abdomen, skin color, Presence of any surgical scar, and presence of any mass lump or not, Umbillicans should also be inspected.
Palpation
- After proper inspection of the patient’s perform abdomen palpation with warm hands. Palpation is done in every region of the abdomen with the flat of the hand.
- Palpating for any tenderness or rebound tenderness.,
- High pressure to assess for tenderness.
- Firm pressure is to assess for the presence of deep swelling and for organ palpation like liver and kidneys.
Percussion
percussion is useful in assessing tenderness. The general abdomen percussion sound is resonant. Different organs possess different different percussion sounds. Percussion is done by hand, by keeping the middle finger on the abdomen and striking it with the middle finger of the subsequent hand. For example In ascites shifting dullness and fluid thrill is positive.
Auscultation
Auscultation is the process of hearing the normal peristaltic activity of the gut using a stethoscope. The stethoscope is placed over the abdominal wall (right to the umbilicus). On auscultating abdomen, the gurgling sound is heard every 5- 10 seconds. This sound is known as Barborygmus. It helps to find out the normal peristaltic activity of the gut or whether they are increased decreased or absent.
