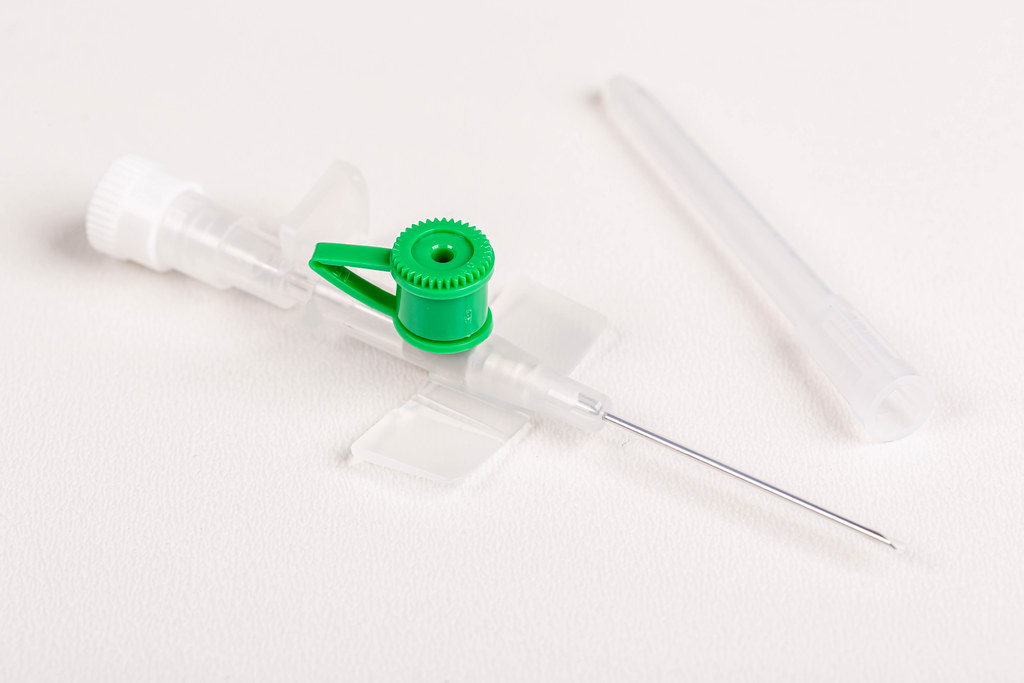
I.V. cannula
An I.V. cannula is a small plastic tube inserted into the veins of the hand or arms. They are often used for different medical procedures like the administration of intravenous fluid like Normal Saline (NS), Ringer Lactate (RL), and (Dextrose Normal Saline) directly in the blood, and the removal of fluid and collection of samples for laboratory examinations. There are cannulas of different sizes providing different fluid transfer capacities ranging from 14 G to 26 G. Cannula size begins from 14G (large size) to 26G (small). The cannula is present with different color coding.
Cannula size
Cannula is available in 7 different sizes. Different sizes of cannula are in use for pediatric groups, young, and adults. In children and elderly patients mostly 22G, 24G, and 26G sizes are used. In adults,14G to 20G cannulas are used as needed. Some different sizes with color coding are mentioned below.
- 14G- Orange
- 16G- Grey
- 18G- Green
- 20G- Pink
- 22G- Blue
- 24G- Yellow
- 26G- Violet
These different sizes of cannulas are used in different patients with different necessities.
- 16–18G for rapid transfusions of fluid in adults.
- 20-22G for routine transfusions in adults like medication.
- 22G-24G is recommended for pediatric use.
- 24G-26 G for Infants and Neonates.
Types of Cannula and Uses
During different medical procedures, different sizes of cannula are used. Different cannulas have different flow rates of fluid making them different from each other. Here are mentioned some basic uses of cannula.
- 14G
- use for massive trauma situations like severe RTA.
- rapid blood transfusions.
- During surgical procedures.
2. 16G and 18G
- During traumatic conditions
- large volume fluid transfusion like hypovolemic shock and severe postpartum hemorrhage (PPH).
3. 20G
- The most commonly used cannula
- For regular medication in admitted patients and patients receiving infusion treatment.
4. 22G
- Patients with small veins, and elderly patients with slippery veins.
- Pediatric and neonate patients.
5. 24G and 26G
- Very fragile and highly mobile small veins
- Neonate patients and pediatric groups.
Cannula size and color
- 14 Gauge
- Color code: Orange
- Diam: 2.1mm
- length in mm: 45
- Flow rate: 240ml/ min
2. 16 Gauge
- Color code: Grey
- Diam: 1.8mm
- length in mm: 45
- Flow rate: 180ml/ min
3. 18 Gauge
- Color code: Green
- Diam: 1.3mm
- length in mm: 32
- Flow rate: 90ml/ min
4. 20 Gauge
- Color code: Pink
- Diam: 1.1mm
- length in mm: 32
- Flow rate: 60 ml/ min
5. 22 Gauge
- Color code: Blue
- Diam: 0.9mm
- length in mm: 25
- Flow rate: 36ml/ min
6. 24 Gauge
- Color code: Yellow
- Diam: 0.7mm
- length in mm: 19
- Flow rate: 20ml/ min
7. 26 Gauge
- Color code: violet
- Diam: 0.6
- length in mm: 19
- Flow rate: 13ml/ min
IV Cannula parts
The simple-looking IV cannula has many parts that are equally important in their role for iv fluid administration. The IV cannula consist of 8 part which are as follows.
- Needle
- Catheter
- Wings
- Injection port caps
- valve
- Needle holder
- Flashback chamber
- Cap or port
Cannulization
Cannulization is the process of inserting an IV catheter in the vein of the human body for different purposes like IV fluid administration, Collection of blood samples, and medication. Before introducing Cannula in the vein aseptic precautions need to be strictly followed. The easy guide to inserting a cannula is mentioned below
Material required
- Disposable gloves
- Hand sanitizer
- Cotton
- Alcohol spirit swab
- Tourniquet
- Cannula of suitable size
- Adhesive tape
Procedures.
- Patient consent is mandatory.
- Wear disposable Gloves.
- Ask the patient to sit down comfortably.
- Identify the suitable vein of the hand or forearm, Vein must be straight and should be suitable for the selected cannula size.
- Tie the tourniquet 5-10 cm above the targeted vein.
- Aseptic precaution is needed i.e. area must be cleaned with the alcohol spirit swab.
- Open the Cannula and check for any defects in the catheter and needle.
- Hold the handle properly and insert the Cannula at a proper 15 to 30-degree angle with the vein.
- After inserting the 1/3rd part of the catheter check whether the catheter is at the vein or not by looking at the Flashback chamber.
- Withdraw the needle slightly back and advance the catheter completely in the vein.
- Release the tourniquet .
- Withdraw the needle completely by preventing the flow back of blood and cap the catheter properly.
- Secure the cannula with adhesive dressing tapes properly.
- Ensure proper functioning by pushing the line with Saline.
- Dispose the waste products and needles properly.
