No, not all the glands produce hormones only endocrine glands produce hormones whereas exocrine glands produce enzymes, mucus, sebum, sweat, etc.
Let’s explore more about the endocrine glands and hormones that act coordinately with the nervous system to make the human body work functionally.
Glands are a special type of tissue capable of producing a special secretion. Some glands are present with ducts whereas some are ductless. The gland with ducts is known as the Exocrine glands. The glands without ducts are known as Endocrine glands. The combined gland is known as mixed glands. The pancreas is a mixed gland that secretes insulin as an endocrine and digestive enzymes as exocrine functions. The endocrine glands are explained below.
- Pituitary gland
- Pineal Gland
- Thyroid Gland
- Parathyroid Gland
- Adrenal Gland
- Pancreas( Islets of Langerhans)
- Testes
- Ovary
- Thymus Glands
Pituitary Glands
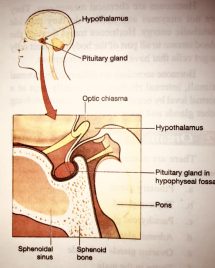
The pituitary gland is a master gland located at the base of the brain in the hypophyseal fossa of the sphenoid bone. It controls the secretion of all the endocrine glands. But the Pituitary gland itself is under the control of the Hypothalamus. Pituitary glands have mainly two parts.
– Anterior pituitary glands
– Posterior Pituitary glands
These two parts are structurally and functionally different. A small avascular structure called Pars Intermedia is known as the intermediate lobe of the brain
Anterior Pituitary Gland
The largest part of the pituitary gland consists of glandular tissue. The hormones secreted by the anterior pituitary glands are of two different types:
- Controlling the function of other endocrine glands.
- Controlling the targeted organs.
Hormones of Anterior Pituitary glands
- Somatotrophic hormone( Growth hormone)
- Thyroid Stimulating Hormone
- Adrenocorticotrophic Hormone
- Follicle Stimulating Hormone
- Luteinizing Hormone
- Prolactin Hormone
Hormones of Posterior Pituitary Gland
- Oxytocin Hormone
- Antidiuretic Hormone
Hormones of Intermediated lobe of Pituitary gland
- Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone
Difference between Endocrine and Exocrine glands.
Features
Endocrine glands
Exocrine glands
- Duct
- Secretion
- Route of secretion
- Quantity of secretion
- Site of secretion and action
- Examples
- They are ductless glands.
- The secretion of endocrine glands is hormones.
- The secretions are released directly into the blood.
- The endocrine gland may be situated a distance away from the site of action.
- The secretions are in large quantities, a small change in secretion leads to disorder.
- The pituitary gland, Thyroid gland, testes, and ovary are examples of endocrine glands.
- They are the duct glands.
- The secretion of exocrine glands is enzymes.
- The secretions are released through a duct to the site of action.
- The exocrine glands are situated near the site of action.
- The secretions are in minute quantity, a small change in secretion leads to no problem.
- Salivary glands, and gastric glands, are examples of exocrine glands.
What are hormones and enzymes?
Hormones are the chemical messengers of the body secreted by the endocrine gland directly into the blood targeting the specific cells in the human body.
Enzymes are the secretion of the exocrine glands that are released into the ducts and act on the site of action.
Difference between Hormones and Enzymes.
Hormones
Enzymes
- They are the secretions of endocrine glands.
- They are carried by blood to the targeted organs.
- They have no molecular weight.
- They are produced on one side and carried by blood to another site for action.
- Their act of reaction is slow.
- They are released in small amounts.
- Excess or deficiency of hormones leads to disorders.
- They initiate the chemical reaction.
- Examples are Insulin, FSH(Follicular Stimulating Hormone), testosterone etc.
- They are the secretions of exocrine glands.
- They are carried by ducts to their site of action.
- They have high molecular weight.
- They may act at the site where they are produced.
- Their reaction is fast.
- They are released in large amounts.
- Excess or deficiency of enzymes leads to the catalyzing of reaction.
- They are the biological catalysts of the human body.
- Examples are Amylase, Lipase, and trypsin.
Classification of hormone
Hormones can be broadly classified into 4 major types which are as follows.
Hormones can be broadly classified into 4 major types based on their component of formation. They are mentioned below.
- Steroids
– Adrenal cortical hormones
– Sex hormones
* Male sex hormones(Estrogen)
* Female sex hormones(Progesterone and Estrogen) - Peptide hormone
– Insulin
– Glucagon - Aminoacid derivative
-Thyroid hormones, thyroxine, and tri-iodothyronine - Fatty acid derivative
– Prostaglandins
