Position of the Human Body
To describe the body and to indicate the location of different organs and parts of the body scientists use several terms of position, direction, and plane of the body.
There are several positions of the human body which are as follows;
- Anatomical position
- Supine position
- Prone Position
- lateral position
- Lithotomy Position
- Dorsal recumbent position
- Sim’s Position
Anatomical position
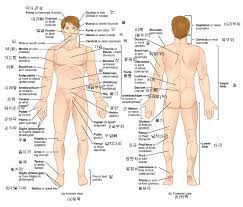
The position of the body in which the person stands erect, with the head straight eyes looking forward, toes directed forward, heel and toes together, and upper limbs hanging on the sides with palm faces forward.
Supine position
The position in which the body is lying down with the face directed upwards. The supine position is useful in surgical procedures, as it grants access to the abdominal region, and thoracic parts like the lungs, and heart as well as the head, neck, and upper and lower extremities.
Prone position
The exact opposite position of the supine position. The body is in a lying down position with the face directed downwards without more flexion, extension with flexed elbows. The palm faces downward maintaining proper alignment of arms and wrists. The prone is useful during the surgery of the dorsal region of the patient’s body
Prone position uses
1. To perform different surgical procedures like spine and neck surgeries, neurosurgeries, and vascular surgeries.
2. Perfect ventilation and improvement in oxygenation.
During surgical procedures of the patient, the breast and abdomen are free from the pressure so the patient won’t have to suffer a complication. The patient’s eye should not bear direct pressure. High alertness of the surgical staff is important during such procedures.
Complications associated with prone position
- Increased abdominal pressure
- Increased bleeding
- Nerve injuries
- Ocular injuries
- Venous air embolism
Lithotomy Position
The position in which the patient is lying supine with buttocks at the edge of the table with hip and knee fully flexed and feet strapped in a position. This position is also the delivery position. It is common for surgical procedures and medical examination of reproductive organs in the pelvis and lower abdomen. This position is common mostly during childbirth. It provides provides good visual and physical access to the perineal area.
Dorsal lithotomy position
The position in which the patient lies on their back with their legs elevated and flexed at hips and knees. It is the same as the lithotomy position but here the patient’s back is in the horizontal orientation.
Semi lithotomy position
The position in which the patient’s legs are also elevated and flexed at the hip and knees. Usually with a lesser degree of elevation than the lithotomy position. The feet are normally closer to the level of the hips, and the abduction movement of the thigh is less in comparison to the lithotomy position. They are commonly used for pelvic area examination urological examination, catheterization, and minor gynecological procedures.
Lateral position
The position in which the patient lying down with one side turning of the body either right or left is the lateral recumbent position.
Left lateral Position
The position in which the patient is lying down on their left side with legs straight or bent. The left hand may be placed under the head for support to the head. The right one rests on the right side.
These are commonly in use for postoperative relief and pain relief for hemorrhagic control. During pregnancy, the left lateral position improves fetal oxygenation.
Right Lateral position
The position in which the patient is lying down on the right side with the left side facing upwards and legs straight or bent. The right hand may be placed under the head for support to the head. The left one rests on the left side.
Dorsal Recumbent position
The position in which the patient is lying down with both legs separated, and knees flexed. The soles of the feet are resting flat on the bed close to the buttocks. The term dorsal means ‘back’.
Sim’s position
The Sims position is named after the famous gynecologist J.marion Sims. It is the halfway position between a lateral and prone position. The patient’s left foot is extended, along the back; the right arm is in front of the patient and vice versa. It is commonly in use for rectal examination and examining women with vaginal wall prolapse.

Wonderful👏